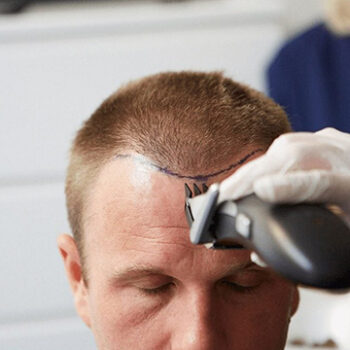
Sweating After a Hair Transplant
Sweating after a hair transplant is a common concern for many patients. Since the scalp is a sensitive area following the procedure, excessive sweating can lead to complications that hinder the healing process and potentially affect the success of the transplant. Understanding the dangers of sweating post-surgery and taking the necessary precautions is essential for ensuring optimal recovery. In this article, we will explore the risks associated with sweating after a hair transplant and offer practical tips to minimize the effects.
The Dangers of Sweating After Hair Transplantation and Precautions Patients Should Take Regarding Sweating
After undergoing a hair transplant, patients are often advised to avoid sweating, particularly during the first few weeks of recovery. Sweating can introduce bacteria to the newly transplanted grafts, cause irritation, and potentially disrupt the healing process. In this section, we’ll outline the key dangers of sweating post-hair transplant and offer helpful advice on how to reduce its occurrence during the recovery period.
The Dangers of Sweating After a Hair Transplant
Excessive sweating after a hair transplant can lead to several complications that might negatively affect the results of the procedure. Below are the primary risks associated with sweating after hair transplant surgery:
1. Risk of Infection:
One of the primary dangers of sweating after a hair transplant is the increased risk of infection. Sweat contains moisture and bacteria that can potentially reach the newly transplanted hair follicles. The scalp is especially vulnerable during the initial recovery period, as the grafts are still in the process of settling and healing. If bacteria enter the area, it could lead to infections, scarring, or other complications that affect the overall success of the hair transplant.
2. Displacement of Grafts:
During the first few days following a hair transplant, the grafts are fragile and need time to properly attach to the scalp. Excessive sweating can cause the grafts to shift or even dislodge from their intended location. This can lead to irregular hair growth or areas where the transplanted hair fails to grow altogether, ultimately affecting the aesthetic results of the transplant.
3. Slower Healing Process:
Sweating can interfere with the natural healing process by prolonging the recovery time. The moisture from sweat can irritate the scalp, making it difficult for the grafts to adhere securely and for the skin to heal properly. The more irritated the scalp becomes, the slower the healing process, which can delay hair growth and affect the final results of the transplant.
4. Discomfort and Itching:
Excessive sweating can lead to increased discomfort and itching in the scalp. When the sweat accumulates, it can cause the newly transplanted area to feel tight, dry, or inflamed. This irritation can be distracting, making it difficult for patients to follow post-operative instructions and maintain a clean, protected scalp.
Measures to Reduce Sweating After a Hair Transplant
To minimize the risks associated with sweating after a hair transplant, there are several measures patients can take to reduce sweating and ensure a smooth recovery:
1. Avoiding Hot and Humid Environments:
After a hair transplant, it is crucial to avoid exposure to hot and humid environments. High temperatures can trigger excessive sweating, making it harder for the scalp to heal. Patients should stay away from saunas, hot tubs, and other areas with high heat or humidity for at least two weeks after the procedure. If exposure to heat is unavoidable, try to keep the head cool and hydrated.
2. Limiting Physical Activity:
Engaging in physical activities that increase heart rate and promote sweating, such as intense exercise or heavy lifting, should be avoided for the first two weeks after a hair transplant. Physical exertion raises the body’s temperature and stimulates sweating, which can increase the risk of infection and graft displacement. Light activities such as walking may be permissible, but it’s important to consult your surgeon before resuming any strenuous exercise.
3. Keeping the Head Elevated:
Sleeping with the head elevated can help reduce swelling and minimize sweating. This is especially important in the early days following a hair transplant. By keeping the head elevated with extra pillows or a specialized wedge, you can prevent fluid buildup and reduce sweating around the transplant area. This simple measure can help to ensure that the grafts remain undisturbed during the recovery period.
4. Choosing the Right Clothing:
Wearing lightweight, breathable clothing can help regulate body temperature and minimize sweating. It’s also important to wear loose-fitting hats or scarves when outdoors to protect the scalp from excessive heat and sun exposure. Avoid tight headgear that could increase sweating around the scalp. Opt for fabrics that are moisture-wicking and comfortable to wear.
5. Using Antiperspirant Products:
While it is essential to avoid applying antiperspirants directly on the scalp after a hair transplant, there are gentle, dermatologist-recommended antiperspirant products available that can be used on other parts of the body to manage sweating. If sweating remains a concern, consulting your doctor for safe alternatives is advisable.

 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Türkçe
Türkçe 中國人
中國人