Receding Hairline in Black Men
Hair loss affects men across all ethnicities, but receding hairlines in Black men present unique considerations due to differences in hair texture, scalp health, cultural significance, and treatment approaches. Understanding these distinctive factors is crucial for Black men seeking to address hairline recession effectively and confidently.
Understanding Black Hair Structure and Its Vulnerability
Black hair has several structural characteristics that make it both resilient and vulnerable in different ways:
- Naturally curly structure: Black hair typically grows in tight coils or curls, which makes it stronger against certain types of damage but more susceptible to others.
- Lower sebum distribution: The curved hair shaft makes it more difficult for natural oils (sebum) to travel from the scalp to the ends, often resulting in drier hair and scalp conditions.
- Fragile hair shaft: Despite its coarse appearance, Afro-textured hair can be quite fragile, particularly at the points where the hair curves or bends.
These unique properties influence how receding hairlines manifest and progress in Black men and have important implications for prevention and treatment.
Common Causes of Hairline Recession in Black Men
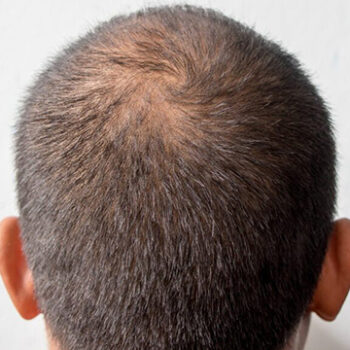
1. Androgenetic Alopecia (Male Pattern Baldness)
Male pattern baldness affects approximately 50-80% of men of all ethnicities throughout their lifetime, and Black men are no exception. This genetic predisposition causes:
- Gradual recession at the temples, creating an “M” shape
- Thinning at the crown
- Progressive hair loss that can eventually connect the receding hairline with crown thinning
In Black men, androgenetic alopecia may manifest slightly differently:
- The pattern often begins at the temples but may progress more evenly across the hairline
- Thinning might appear as a general decrease in density rather than complete baldness in affected areas
- The distinctive curl pattern can sometimes partially mask early thinning
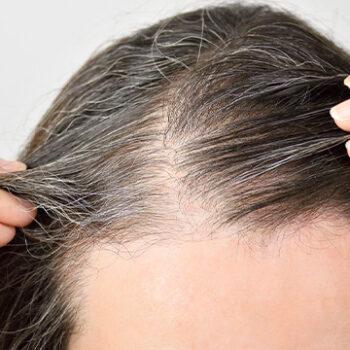
2. Traction Alopecia
Particularly relevant for Black men is traction alopecia, which accounts for up to 17% of hair loss cases in the Black community. This condition results from hairstyling practices that place chronic tension on the hair follicles:
- Tight braids or cornrows
- Dreadlocks that are too heavy or tight
- Regular use of du-rags or caps worn too tightly
- High-tension hairlines from certain fade styles that require frequent maintenance
The hairline is especially vulnerable to traction forces, making it a common site for this type of hair loss. Early traction alopecia is often reversible, but chronic tension can lead to permanent follicle damage and hairline recession.
3. Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia (CCCA)
Originally termed “hot comb alopecia,” CCCA was once thought to exclusively affect Black women. However, dermatologists now recognize that it affects Black men as well, though less frequently. This inflammatory condition:
- Begins at the crown but can spread to affect the hairline
- Causes scarring of hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss
- May be triggered by certain chemical hair treatments or thermal styling
- Often goes undiagnosed in earlier stages when intervention would be most effective
4. Seborrheic Dermatitis and Other Scalp Conditions
Black men experience higher rates of certain scalp conditions that can contribute to hairline recession:
- Seborrheic dermatitis: Characterized by scalp inflammation, flaking, and itching, this condition affects approximately 10% of the population but is more common in Black individuals.
- Folliculitis: Inflammation of hair follicles, often due to bacterial infection, can be more prevalent due to certain grooming practices.
- Pseudofolliculitis barbae: Often called “razor bumps,” this condition results from shaved hair curling back into the skin, causing inflammation that can damage nearby hair follicles at the hairline.
These conditions can create an inhospitable environment for healthy hair growth, particularly along the hairline where they often manifest most prominently.
5. Cultural and Grooming Factors
Several cultural and grooming practices common in Black communities can impact hairline health:
- Chemical treatments: Relaxers and texturizers contain harsh chemicals that can damage the hair shaft and follicle.
- Frequent lineup/edge-up styling: Regular trimming of the hairline for a clean appearance can gradually push the natural hairline back if not done carefully.
- Excessive brushing: Particularly with hard-bristled brushes to achieve certain styles can cause traction and breakage.
- Heat styling: While less common in men, the use of hot combs or excessive heat can damage follicles.
These practices, when performed regularly over time, can contribute to gradual hairline recession even in the absence of genetic predisposition.
Distinguishing Features of Receding Hairlines in Black Men
Understanding the visual patterns of recession can help identify the cause and determine appropriate interventions:
- Genetic recession: Typically symmetrical, beginning at the temples with gradual progression
- Traction-induced recession: Often presents with small bumps, broken hairs, and may show an unusual pattern corresponding to styling tension points
- Inflammatory causes: Usually accompanied by scalp symptoms like redness, scaling, or pustules
Early detection is crucial, as the appropriate intervention depends on correctly identifying the underlying cause.
Treatment and Management Options
Medical Interventions
Several medical treatments can effectively address receding hairlines in Black men:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): Studies show it’s effective for Black hair, though care must be taken as the solution can dry the scalp.
- Finasteride (Propecia): Oral medication that blocks DHT production; efficacy appears consistent across ethnicities.
- Corticosteroid injections: Particularly helpful for inflammatory conditions like CCCA.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: Shows promising results for stimulating follicle regeneration in the hairline region.
When seeking medical treatment, it’s advisable to consult with dermatologists who specialize in ethnic hair, as they will better understand the unique considerations for Black hair.
Lifestyle and Home Care Approaches
Proactive maintenance can significantly impact hairline health:
- Gentle grooming practices: Using wide-tooth combs and avoiding excessive tension
- Scalp care: Regular cleansing with appropriate products to maintain scalp health
- Moisture balance: Using appropriate moisturizers and oils to prevent dryness without causing buildup
- Protective styling: Choosing styles that don’t place tension on the hairline
- Nutrition: Ensuring adequate intake of biotin, iron, protein, and other hair-supporting nutrients
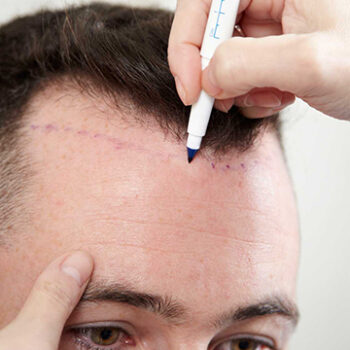
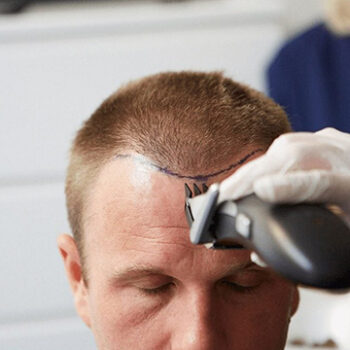
Surgical Options
For advanced hairline recession, surgical approaches might be considered:
- Follicular unit transplantation (FUT): Involves removing a strip of scalp and transplanting individual follicles
- Follicular unit extraction (FUE): Individual follicles are harvested and transplanted without removing a strip of scalp
- Scalp micropigmentation: Creates the appearance of closely-shaved hair through detailed tattooing
Black men considering hair transplantation should seek surgeons experienced with Afro-textured hair, as the curly growth pattern requires specific techniques for natural-looking results.
Embracing Alternative Approaches
For many Black men, embracing hair loss has become a powerful statement:
- The completely shaved head has become a mainstream, fashionable option
- Beard growth (when possible) can balance facial aesthetics when paired with a receding hairline
- Scalp care remains important even when choosing to shave the head
Psychological and Cultural Considerations
Hair carries significant cultural and identity implications in Black communities:
- Historically, different hairstyles have represented cultural pride, resistance, and expression
- Hair loss can impact self-perception and confidence
- Community support and representation of diverse hair patterns can help normalize the experience
When to Seek Professional Help
Black men should consider consulting a dermatologist, preferably one experienced with ethnic hair, when:
- Hair loss progresses rapidly
- Recession is accompanied by symptoms like itching, burning, or pain
- There are visible scalp abnormalities like scaling or inflammation
- Over-the-counter treatments haven’t shown improvement after several months

 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Türkçe
Türkçe 中國人
中國人